By Otmar D. Wiestler, Bernhard Haendler, D. Mumberg
Cancer stem cells have initially been pointed out in leukemia and later in different reliable tumor varieties. they've got very diversified homes from the majority of the tumor as they divide even more slowly and feature very effective drug resistance mechanisms. present remedies may mostly spare melanoma stem cells. This ebook seems at fresh advancements within the box of melanoma stem cells and the prospective effect for the id of novel remedy paradigms for cancer.
Read Online or Download Cancer stem cells : novel concepts and prospects for tumor therapy PDF
Similar cell biology books
Telomerases, telomeres, and cancer
This quantity offers huge insights to the newest discoveries in telomere biology, with present functions in tumor diagnostics and destiny potentials in treatment. particular gains of numerous organisms are offered, with ciliates, the "telomerase discoverer organisms"; yeasts, the "molecular genetisists' toy for eukaryotes"; together with crops and bugs to boot.
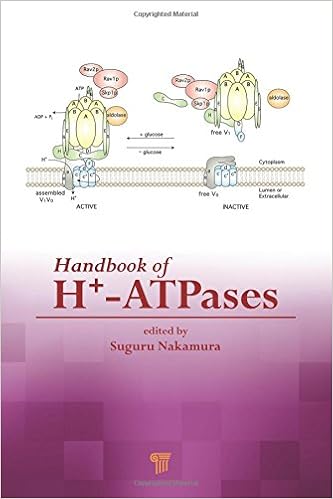
This guide on vacuolar and plasma membrane H+-ATPases is the 1st to target a necessary hyperlink among vacuolar H+-ATPase and the glycolysis metabolic pathway to appreciate the mechanism of diabetes and the metabolism of melanoma cells. It provides fresh findings at the constitution and serve as of vacuolar H+-ATPase in glucose selling meeting and signaling.
Microglia Biology, Functions and Roles in Disease
The pioneering stories by means of numerous prime researchers within the early a part of the final century first defined the lifestyles of microglial cells either within the early mind improvement and in pathological stipulations. Microglial cells have been later demonstrated to be the resident mind macrophages and immunocompetent cells current ubiquitously within the imperative frightened approach together with the retina in organization with different glial cells, neurons and blood vessels.
Most sensible Investigators discover the Complexities of Angiogenesis melanoma learn The focusing on of tumor angiogenesis has developed into some of the most generally pursued healing options. even though, as of but, no antiangiogenic agent used as a monotherapy has established a survival profit in a randomized section III trial.
- mateo protein-lipid interactions-new approaches and emerging concepts
- Chromatin and Gene Regulation: Molecular Mechanisms in Epigenetics
- Molecular Aspects of Aging : Understanding Lung Aging
- Caenorhabditis elegans : modern biological analysis of an organism
- Cancer Stem Cells
- The Encyclopedia of Cell Technology, 2 Volume Set (Wiley Biotechnology Encyclopedias)
Additional info for Cancer stem cells : novel concepts and prospects for tumor therapy
Sample text
2004; Korinek et al. 1998; Lai et al. 2003; Machold et al. 2003; Owens and Watt 2003; Pinto et al. 2003; Perez-Losada and Balmain 2003; Polesskaya et al. 2003; Ramalho-Santos et al. 2000; Reya et al. 2003; Zhang and Kalderon 2001). For example, studies of transgenic mice suggest that activation of the Wnt pathway in epidermal stem cells may lead to epithelial cancers (Gat et al. 1998). It was found consistently that gene expression patterns in colon cancer cells and colon stem cells resembled one another (van de Wetering et al.
Moreover, cancer cells expressing Wnt-1 are resistant to therapies that mediate apoptosis (Chen et al. 2001). Overexpression of Wnt-1 has been demonstrated in NSCLC cell lines and primary cancer tissues (He et al. 2004). Blockade of Wnt-1 signaling induces apoptosis in vitro 38 B. M. Jablons and suppresses tumor growth in vivo (He et al. 2004). Similar results were observed in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (Rhee et al. 2002), suggesting that Wnt-1 signaling is a key mediator of apoptosis in epithelial cancers.
It was found consistently that gene expression patterns in colon cancer cells and colon stem cells resembled one another (van de Wetering et al. 2002). Other evidence points as well to Wnt pathway involvement in stem cell development. Treatment of isolated HSCs with Wnt proteins in vitro increases their proliferative capacity and improves their ability to form colonies, both in vitro and in vivo (Reya et al. 2003). While inhibiting Wnt pathway activation in the intestine fails to prevent the development, initially, of normal epithelial architecture, its inactivation eventually results in a progressive degradation of epithelial structure.