By Paul Blum
Even though they contain one of many 3 primary branches of lifestyles, it was once in basic terms the decade that Archaea have been officially well-known as a gaggle along Eukaryotes and micro organism. Bacteria-like in that they're unmarried celled organisms that lack a nucleus and intracellular organelles, the Arachaea additionally percentage a wide gene set regular of eukaryotes, for making and repairing DNA, RNA and protien. extra unusually, they simply inhabit environments normal of the extremes of early earth--hot springs, thermal ocean vents, saline lake, or oxygen poor sediments. A breakpoint at the universal evolutionary direction, it really is obtrusive that the Archaea diverged early within the background of existence, constructing thier significance in evolutionary sciences. Archaea: old Microbes, severe Environments, and the starting place of existence tells this evolving tale, furthering our knowing of the microbe commonalities, and delivering for evolutionary justification within the use of archaea as mechanistic version platforms. Key positive factors* presents a special and present precis of universal subcellular mechanisms in archaea and eukaryotes* Emphasizes using genomics to supply a organic context for realizing archaea* Contrasts evolutionary experiences at the fossil checklist with these on molecular phylogeny* contains broad tables, graphs, photos, drawings and different illustrations* Simplifies the interdisciplinary problem essential to comprehend the importance of archaea
Read or Download Ancient Microbes, Extreme Environments, and the Origin of Life PDF
Similar cell biology books
Telomerases, telomeres, and cancer
This quantity presents huge insights to the latest discoveries in telomere biology, with present functions in tumor diagnostics and destiny potentials in treatment. specified positive factors of numerous organisms are offered, with ciliates, the "telomerase discoverer organisms"; yeasts, the "molecular genetisists' toy for eukaryotes"; together with crops and bugs in addition.
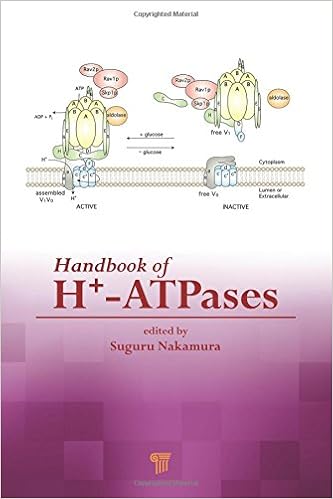
This guide on vacuolar and plasma membrane H+-ATPases is the 1st to target a vital hyperlink among vacuolar H+-ATPase and the glycolysis metabolic pathway to appreciate the mechanism of diabetes and the metabolism of melanoma cells. It offers fresh findings at the constitution and serve as of vacuolar H+-ATPase in glucose selling meeting and signaling.
Microglia Biology, Functions and Roles in Disease
The pioneering reviews via numerous prime researchers within the early a part of the final century first defined the lifestyles of microglial cells either within the early mind improvement and in pathological stipulations. Microglial cells have been later validated to be the resident mind macrophages and immunocompetent cells current ubiquitously within the crucial worried process together with the retina in organization with different glial cells, neurons and blood vessels.
Best Investigators discover the Complexities of Angiogenesis melanoma examine The focusing on of tumor angiogenesis has advanced into some of the most largely pursued healing concepts. even though, as of but, no antiangiogenic agent used as a monotherapy has established a survival profit in a randomized part III trial.
- Regenerating the Heart: Stem Cells and the Cardiovascular System
- The Mitotic Spindle: Methods and Protocols
- Chromatin and Gene Regulation: Molecular Mechanisms in Epigenetics
- Regenerating the Heart: Stem Cells and the Cardiovascular System
- The Biochemistry of Cell Signalling
- Principles of Cellular, Molecular, and Developmental Neuroscience
Extra resources for Ancient Microbes, Extreme Environments, and the Origin of Life
Sample text
Sci. Am. 245, 64-73. Gruner, J. W. (1923). J. Geol. 31, 146. Gruner, J. W. J. Geol. 33,151-152. Hawley, J. E. (1926). I: Geol. 34,441-461. Hayes, J. M. (1994). In “Early Life on Earth” (S. ), pp. 220-236. Columbia University Press, New York. Hayes, J. , Kaplan, 1. , et al. (1983). In “Earth’s Earliest Biosphere” (J. W. ), pp. 93-134. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ. Hofmann, H. J. (1972). Proc. 24th Int. Geol. , Sect. 1, pp. 21-30. Hofmann, H. J. (1973). Earth Sci. Rev. 9,339-373. Hofmann, H.
Walter, M. , et al. (1998). Alcheringa 22, 285-314. Westall, E (1999). J. Geaphys. Res. 104(E7), 16437-16451. Wilde, S. , and Valley, J. , et al. (2001). Nature 409, 175-178. , Fischer, W. , et al. (2000). Science 289, 1724-1730. A Comparative Genomics Approach for Studying Ancestral Proteins and Evolution PING LIANG* AND MONICA RILEY Josephine Bay Paul Center for Molecular Evolution and Comparative Marine Biological Laboratory Woods Hole Massachusetts 02543 Biology I. The Genome Era: A Great Opportunity for Evolutionary Biology II.
Science 119,606-608. Walcott, C. D. (1912). Geol. Suq? Can. Mem. 28, 16-23. Walker, J. C. , et al. (1983). In “Earth’s Earliest Biosphere” (J. W. ), pp. 260-290. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ. Walsh, M. M. (1989). “Carbonaceous Cherts of the Swaziland Supergroup, Barberton Mountian Land, Southern Africa,” Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge. Walsh, M. M. (1992). Precambr. Res. 54, 271-293. Walsh, M. , and Lowe, D. R. (1985). Nature 314, 530-532. Developments in Sedimentology. Elsevier, Walter, M.